Introduction
The world economy has entered a new era after 2024 — one defined by rapid technological change, shifting global power dynamics, sustainability goals, and evolving consumer behavior. The pandemic years, geopolitical conflicts, and inflationary pressures have all left deep marks on how economies operate today.
As we move beyond 2024, nations, businesses, and individuals are adapting to a new global economic order. From the rise of green energy and digital currencies to supply chain reconfigurations and artificial intelligence (AI) integration, these trends are rewriting the rules of economic growth and development.
1. Slower but Stable Global Growth
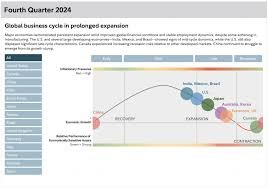
After several years of volatility, the global economy is stabilizing. While growth rates have slowed compared to the pre-pandemic boom, they are becoming more balanced and sustainable.
- Developed economies such as the U.S., Japan, and the EU are seeing moderate growth driven by steady consumer spending and digital investment.
- Emerging markets like India, Vietnam, and parts of Africa are becoming major engines of growth due to young populations, urbanization, and rising tech adoption.
The focus has shifted from fast growth to resilient and inclusive development — creating stability instead of short-term gains.
2. Inflation Control and Monetary Policy Adjustments
The inflation crisis that peaked between 2022 and 2023 has forced central banks worldwide to rethink their policies.
By 2025, many countries have adopted hybrid monetary models — balancing interest rate hikes with digital financial tools to stabilize economies.
- Central banks are introducing digital currencies (CBDCs) to improve transaction efficiency and transparency.
- Inflation is expected to normalize, though food and energy prices may remain slightly elevated due to ongoing supply chain adjustments.

3. The Rise of Green and Sustainable Economies 🌱
One of the strongest post-2024 economic trends is the global shift toward sustainability and green transformation.
Countries are investing billions in clean energy, electric vehicles, recycling systems, and eco-friendly technologies.
- Renewable energy (solar, wind, hydrogen) continues to replace fossil fuels.
- Carbon markets and green bonds are expanding rapidly.
- Corporations are now prioritizing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) standards to attract investors and consumers.
This green revolution is not just about saving the planet — it’s creating millions of new jobs and reshaping industrial policies worldwide.
4. Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
After 2024, technology has become the backbone of economic growth.
- AI and automation are transforming manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and logistics.
- Remote and hybrid work models remain a permanent part of the global economy.
- Digital platforms are empowering small businesses to reach international markets.
However, this technological boom also raises challenges such as job displacement, data privacy, and AI regulation — forcing governments to rethink labor policies and digital ethics frameworks.
5. Shifts in Global Trade and Supply Chains
The economic disruptions of the past years exposed weaknesses in global supply chains. After 2024, countries and corporations are focusing on “supply chain resilience” instead of cheap efficiency.
Key changes include:
- Nearshoring and friend-shoring (moving production closer to home or to allied nations).
- Greater investment in automation and logistics infrastructure.
- Increased regional cooperation — especially in Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
These trends are helping create a more balanced and diversified global trade environment.
6. The Digital Currency and Fintech Revolution 💰
Digital currencies are transforming global finance.
- Many nations are experimenting with CBDCs (Central Bank Digital Currencies) for faster and more secure transactions.
- Cryptocurrencies are becoming more regulated but still serve as an alternative investment option.
- Fintech startups continue to revolutionize payments, lending, and banking — making financial inclusion a global reality.
This digital financial evolution is building the foundation for a more connected and cashless global economy.

7. Geopolitical and Economic Realignments
Global politics and economics are more interconnected than ever.
- The competition between the U.S. and China continues to shape trade, technology, and security policies.
- India is emerging as a major global economic hub, attracting manufacturing and tech investment.
- Africa is becoming the next growth frontier, with its youthful population and growing infrastructure.
At the same time, regional alliances — like BRICS, ASEAN, and the EU — are strengthening to reduce dependency on traditional Western systems.
8. Labor Market Evolution and Skill Transformation
Automation and digitalization are changing how people work.
- Routine jobs are declining, while demand for creative, technical, and AI-related skills is rising.
- Lifelong learning and reskilling programs are becoming essential for job security.
- The gig economy continues to grow, giving workers more flexibility but also less stability.
Governments are working on new labor laws to protect freelancers and remote workers while maintaining innovation.
9. The Role of Innovation and Startups
Startups are playing a vital role in reshaping the post-2024 economy.
Entrepreneurs are driving change in sectors like:
- Fintech
- Health tech
- Edtech
- Clean energy
- E-commerce
Venture capital funding is becoming more selective but still focused on ideas that promote sustainability, inclusivity, and technology-driven solutions.
10. The Growing Importance of Data and Cybersecurity
Data is now the world’s most valuable resource — even more than oil.
After 2024, the global economy heavily depends on data analytics, cloud computing, and secure digital networks.
However, cyber threats are also increasing, pushing companies and governments to strengthen cybersecurity infrastructure and data protection laws.

Conclusion
The economic landscape after 2024 reflects a world in transformation — technological, environmental, and social. While growth may be slower than in past decades, it’s becoming more balanced, inclusive, and sustainable.
The next generation of economic success will belong to those who can adapt — businesses that embrace digitalization, governments that support innovation, and individuals who continuously learn and evolve.
In short, the post-2024 global economy is not just about recovery — it’s about reinvention. 🌎💡
